Draw Rectangles
thumby.display.drawFilledRectangle(x, y, w, h, color) | creates filled rectangle with color at x and y with dimensions w (width) and h (height). Returns None, all parameters required.
x- type: int
- values: 0 (left) ~ 71 (right)
y- type: int
- values: 0 (top) ~ 39 (bottom)
w- type: int
- values: 0 ~ 71
h- type: int
- values: 0 ~ 39
color- type: int
- values: 0 or 1
thumby.display.drawRectangle(x, y, w, h, color) | creates 1px thick outline rectangle with color at x and y with dimensions w (width) and h (height) (thickness not variable). Returns None, all parameters required.
x- type: int
- values: 0 (left) ~ 71 (right)
y- type: int
- values: 0 (top) ~ 39 (bottom)
w- type: int
- values: 0 ~ 71
h- type: int
- values: 0 ~ 39
color- type: int
- values: 0 or 1 -- where 0 is black or an unlit pixel, and 1 is white or a lit pixel
Rectangles Example: Filled and not Filled
When drawing Rectangles, it may be helpful to use the thumby.display.width and thumby.display.height member variables for the screen width (72), and the height (40). Otherwise, you can do the math yourself. This example uses both methods to draw three different rectangles:
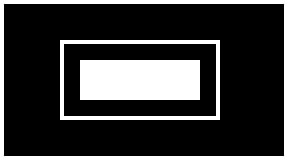
import thumby
thumby.display.fill(0) # Fill canvas to black
# Draw a rectangle around the edge of the screen
thumby.display.drawRectangle(0, 0, thumby.display.width, thumby.display.height, 1) # (x, y, w, h, color)
# Draw a rectangle in the middle of the screen
thumby.display.drawRectangle(15, 10, 40, 20, 1) # (x, y, w, h, color)
# Draw a smaller, filled rectangle inside the other rectangle
thumby.display.drawFilledRectangle(20, 15, 30, 10, 1) # (x, y, w, h, color)
# Update display
thumby.display.update()